With each new version, Windows Server adds new features. Active Directory Domain & Forest Functional Levels determine which features can be used within each system. There exists a simple way to check Forest Functional Levels and Domain and these steps are in this tutorial.
| Did you know? Windows 10 is Microsoft’s latest OS. There are many new tips and tricks that you can learn to improve the user experience. Read: Windows 10 Tutorial. |
What is an Active Directory Domain?
| Did you know? In Windows 2000 Server and Windows Server 2003, the directory service is named Active Directory. In Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2, the directory service is named Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS). The rest of this topic refers to AD DS, but the information is also applicable to Active Directory. |
What are Forest Functional Levels?
Tree
Forest
Trusts
Global Catalog
| Did you know? There is an easy way to Repair MDAC WIN XP SP3. MDAC or Microsoft Data Access Components (MDAC; also known as Windows DAC) is a framework of interrelated Microsoft technologies that allows programmers a uniform and comprehensive way of developing applications that can access almost any data store. Read more about it here. |
How to Check Domain and Forest Functional Level
- From the “Administrative Tools” menu, select “Active Directory Domains and Trusts“.
- Right-click the root domain, then select “Properties“.
- Under the “General” tab, the “Domain functional level” and “Forest functional level” is displayed on the screen.
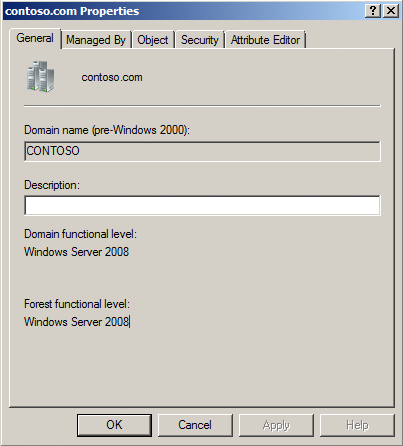
Active Directory: How to Check Domain and Forest Functional Level
How to raise Active Directory domain and forest functional levels
| Did you know? You can now Revert Windows 10 Devices to Windows 7/8/8.1. Check out the guide and learn how to rollback to Windows 7 or 8 from a Windows 10 upgrade. |
Functional levels are an extension of the mixed mode and the native mode concepts that were introduced in Microsoft Windows 2000 Server to activate new Active Directory features. Some additional Active Directory features are available when all the domain controllers are running the newest Windows Server version in a domain or in a forest, and when the administrator activates the corresponding functional level in the domain or in the forest.
To activate the newest domain features, all the domain controllers must be running the newest Windows Server operating system version in the domain. If this requirement is met, the administrator can raise the domain functional level.
To activate the newest forest-wide features, all the domain controllers in the forest must be running the Windows Server operating system version that corresponds to the desired forest functional level. Additionally, the current domain functional level must already be at the newest level. If these requirements are met, the administrator can raise the forest functional level.
Generally, the changes to the domain and forest functional levels are irreversible. If the change can be undone, a forest recovery must be used. With the Windows Server 2008 R2 operating system, the changes to domain functional levels and to forest functional levels can be rolled back. However, the roll back can be performed in only the specific scenarios that are described in the Technet article about the Active Directory functional levels.
Note The newest domain functional levels and the newest forest functional levels affect only the way that the domain controllers operate together as a group. The clients that interact with the domain or with the forest are unaffected. Additionally, applications are unaffected by changes to the domain functional levels or to the forest functional levels. However, applications can take advantage of the newest domain features and of the newest forest features.
For more information, view the TechNet article about the features associated with the various functional levels.
| Did you know? There’s an easy way to Fix “has not passed Windows Logo testing”. Check out the guide and learn how to troubleshoot common errors on Windows computers. |
Raising the functional level
Caution Do not raise the functional level if the domain has or will have a domain controller that is of an earlier version than the version that is cited for that level. For example, a Windows Server 2008 functional level requires that all domain controllers have Windows Server 2008 or a later operating system installed in the domain or in the forest. After the domain functional level is raised to a higher level, it can only be changed back to an older level by using a forest recovery. This restriction exists because the features often change the communication between the domain controllers, or because the features change the storage of the Active Directory data in the database.
The most common method to enable the domain and forest functional levels is to use the graphical user interface (GUI) administration tools that are documented in the TechNet article about Windows Server 2003 Active Directory functional levels. This article discusses Windows Server 2003.However, the steps are the same in the newer the operating system versions. Additionally, the functional level can be manually configured or can be configured by using Windows PowerShell scripts. For more information about how to manually configure the functional level, see the “View and set the functional level” section.
For more information about how to use Windows PowerShell script to configure the functional level, view the TechNet article that discusses this method.
View and set the functional level manually
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) tools such as Ldp.exe and Adsiedit.msc can be used to view and to modify the current domain and forest functional level settings. When you change the functional level attributes manually, the best practice is to make attribute changes on the Flexible Single Master Operations (FSMO) domain controller that is normally targeted by the Microsoft administrative tools.
| Did you know? There’s an easy way to Fix Unidentified Network – No Internet Access Error Windows. Check out the guide and learn how to troubleshoot internet connectivity errors on Windows computers. |
Domain functional level settings
The msDS-Behavior-Version attribute is on the naming context (NC) head for the domain, i.e., DC=corp, DC=contoso, DC=com.
The following are the values that can be set for this attribute:
- Value of 0 or not set=mixed level domain
- Value of 1=Windows Server 2003 domain level
- Value of 2=Windows Server 2003 domain level
- Value of 3=Windows Server 2008 domain level
- Value of 4=Windows Server 2008 R2 domain level
Mixed mode and native mode settings
The ntMixedDomain attribute is on the naming context (NC) head for the domain, i.e., DC=corp, DC=contoso, DC=com.
The following are the values that can be set for this attribute:
- Value of 0=Native level domain
- Value of 1=Mixed level domain
| Did you know? There’s an easy way to carry out a dns_probe_finished_bad_config Fix. Check out the guide and learn how to troubleshoot internet connectivity errors on Windows computers. |
Forest level setting
The msDS-Behavior-Version attribute is on the CN=Partitions object in the Configuration naming context (NC), i.e., CN=Partitions, CN=Configuration, DC=ForestRootDomain.
The following are the values that can be set for this attribute:
- Value of 0 or not set=mixed level forest
- Value of 1=Windows Server 2003 interim forest level
- Value of 2=Windows Server 2003 forest levelNote When you increase the msDS-Behavior-Version attribute from the 0 value to the 1 value by usingAdsiedit.msc, you receive the following error message:
Illegal modify operation. Some aspect of the modification is not permitted.
- Value of 3=Windows Server 2008 domain level
- Value of 4=Windows Server 2008 R2 domain level
After you use the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) tools to edit the functional level, click OK to continue. The attributes on the partitions container and on the domain head are correctly increased. If an error message is report by the Ldp.exe file, you can safely ignore the error message. To verify that the level increase was successful, refresh the attribute list, and then check the current setting. This error message may also occur after you have performed the level increase on the authoritative FSMO if the change has not yet replicated to the local domain controller.
Quickly view the current settings by using the Ldp.exe file
- Start the Ldp.exe file.
- On the Connection menu, click Connect.
- Specify the domain controller that you want to query, or leave the space blank to connect to any domain controller.
After you connect to a domain controller, the RootDSE information for the domain controller appears. This information includes information on the forest, domain, and domain controllers. The following is an example of a Windows Server 2003-based domain controller. In the following example, assume that the domain mode is Windows Server 2003 and that the forest mode is Windows 2000 Server.
| Did you know? There’s an easy way to Fix dns_probe_finished_nxdomain Error. Check out the guide and learn how to troubleshoot internet connectivity errors on Windows computers. |
Note The domain controller functionality represents the highest possible functional level for this domain controller.
- 1> domainFunctionality: 2=(DS_BEHAVIOR_WIN2003)
- 1> forestFunctionality: 0=(DS_BEHAVIOR_WIN2000)
- 1> domainControllerFunctionality: 2=(DS_BEHAVIOR_WIN2003)
Requirements when you manually change the functional level
- You must change the domain mode to native mode before you raise the domain level if one of the following conditions is true:
- The domain functional level is programmatically raised to the second functional level by directly modifying the value of themsdsBehaviorVersion attribute on the domainDNS object.
- The domain functional level is raised to the second functional level by using the Ldp.exe utility or the Adsiedit.msc utility.
If you do not change the domain mode to native mode before you raise the domain level, the operation is not completed successfully, and you receive the following error messages:
SV_PROBLEM_WILL_NOT_PERFORM
ERROR_DS_ILLEGAL_MOD_OPERATIONAdditionally, the following message is logged in the Directory Services log:
Active Directory could not update the functional level of the following domain because the domain is in mixed mode.
In this scenario, you can change the domain mode to native mode by using the Active Directory Users & Computers snap-in, by using the Active Directory Domains & Trusts UI MMC snap-in, or by programmatically changing the value of the ntMixedDomainattribute to 0 on the domainDNS object. When this process is used to raise the domain functional level to 2 (Windows Server 2003), the domain mode is automatically changed to native mode.
- The transition from mixed mode to native mode changes the scope of the Schema Administrators security group and the Enterprise Administrators security group to universal groups. When these groups have been changed to universal groups, the following message is logged in the System log:
Event Type: Information
Event Source: SAM
Event ID: 16408
Computer: Server Name
Description: “Domain operation mode has been changed to Native Mode. The change cannot be reversed.” - When the Windows Server 2003 administrative tools are used to invoke the domain functional level, both the ntmixedmode attribute and the msdsBehaviorVersion attribute are modified in the correct order. However, this does not always occur. In the following scenario, the native mode is implicitly set to a value of 0 without changing the scope for the Schema Administrators security group and the Enterprise Administrators security group to universal:
- The msdsBehaviorVersion attribute that controls the domain functional mode is manually or programmatically set to the value of 2.
- The forest functional level is set to 2 by using any method.
In this scenario, the Domain controllers block the transition to the forest functional level until all of the domains that are in the local area network are configured to native mode and the required attribute change is made in the security group scopes:.
| Did you know? There’s an easy way to do an ERR_NAME_RESOLUTION_FAILED Fix – Solution. Check out the guide and learn how to troubleshoot internet connectivity errors on Windows computers. |
Functional levels relevant to Windows 2000 Server
Windows 2000 Server supports only mixed mode and native mode. Additionally, it only applies these modes to the domain functionality. The following sections list the Windows Server 2003 domain modes because these modes affect how Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 2000 Server domains are upgraded.
There are a number of considerations when raising the operating system level of the domain controller. These considerations are caused by the storage and replication limitations of the linked attributes in Windows 2000 Server modes.
Windows 2000 Server mixed (default)
- Supported domain controllers: Microsoft Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000 Server , Windows Server 2003
- Activated features: local and global groups, global catalog support
Windows 2000 Server native
- Supported domain controllers: Windows 2000 Server, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2
- Activated features: group nesting, universal groups, Sid History, converting groups between security groups and distribution groups, you can raise domain levels by increasing the forest level settings
Windows Server 2003 interim
- Supported domain controllers: Windows NT 4.0, Windows Server 2003
- Supported features: There are no domain-wide features activated at this level. All domains in a forest are automatically raised to this level when the forest level increases to interim. This mode is only used when you upgrade domain controllers in Windows NT 4.0 domains to Windows Server 2003 domain controllers.
Windows Server 2003
- Supported domain controllers: Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2
- Supported features: domain controller rename, logon timestamp attribute updated and replicated. User password support on the InetOrgPerson objectClass. Constrained delegation, you can redirect the Users and Computers containers.
Domains that are upgraded from Windows NT 4.0 or created by the promotion of a Windows Server 2003-based computer operate at the Windows 2000 mixed functional level. Windows 2000 Server domains maintain their current domain functional level when Windows 2000 Server domain controllers are upgraded to the Windows Server 2003 operating system. You can raise the domain functional level to either Windows 2000 Server native or Windows Server 2003.
Interim level – upgrade from a Windows NT 4.0 domain
Windows Server 2003 Active Directory permits a special forest and domain functional level that is named Windows Server 2003 interim. This functional level is provided for upgrades of existing Windows NT 4.0 domains where one or more Windows NT 4.0 backup domain controllers (BDCs) must function after the upgrade. Windows 2000 Server domain controllers are not supported in this mode. Windows Server 2003 interim applies to the following scenarios:
- Domain upgrades from Windows NT 4.0 to Windows Server 2003.
- Windows NT 4.0 BDCs do not upgrade immediately.
- Windows NT 4.0 domains that contain groups with more than 5000 members (excluding the domain users group).
- There are no plans to implement Windows Server2000 domain controllers in the forest at any time.
Windows Server 2003 interim provides two important enhancements while still permitting replication to Windows NT 4.0 BDCs:
- Efficient replication of security groups, and support for more than 5000 members per group.
- Improved KCC inter-site topology generator algorithms.
Because of the efficiencies in group replication that is activated in the interim level, the interim level is the recommended level for all Windows NT 4.0 upgrades. See the “Best Practices” section of this article for more details.
Setting Windows Server 2003 interim forest functional level
Windows Server 2003 interim can be activated in three different ways. The first two methods are highly recommended. This is because security groups use linked value replication (LVR) after the Windows NT 4.0 domain’s primary domain controller (PDC) has been upgraded to a Windows Server 2003 domain controller. The third option is less highly recommended because membership in security groups uses a single multi-valued attribute which may result in replication issues. The ways in which Windows Server 2003 interim can be activated are:
- During the upgrade.The option is presented in the Dcpromo installation wizard when you upgrade the PDC of a Windows NT 4.0 domain that serves as the first domain controller in the root domain of a new forest.
- Before you upgrade the Windows NT 4.0 PDC of a Windows NT 4.0 as the first domain controller of a new domain in an existing forest by manually configuring the forest functional level by using Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) tools.Child domains inherit the forest-wide functionality settings from the forest they are promoted into. Upgrading the PDC of a Windows NT 4.0 domain as a child domain in an existing Windows Server 2003 forest where interim forest functional levels had been configured by using the Ldp.exe file or the Adsiedit.msc file permits security groups to use linked value replication after the operating system version upgrade.
- After the upgrade by using LDAP tools.Use the last two options when you join an existing Windows Server 2003 forest during an upgrade. This is a common scenario when an “empty root” domain is in position. The upgraded domain is joined as a child of the empty root and inherits the domain setting from the forest.
Best practices
The following section discusses the best practices for increasing functional levels. The section is broken into two parts. “Preparation Tasks” discusses the work that you must do before the increase and “Optimal Paths Increase” discusses the motivations and methods for different level increase scenarios.
To discover Windows NT 4.0 domain controllers, follow these steps:
- From any Windows Server 2003-based domain controller, open Active Directory Users and Computers.
- If the domain controller is not already connected to the appropriate domain, follow these steps to connect to the appropriate domain:
- Right-click the current domain object, and then click Connect to domain.
- In the Domain dialog box, type the DNS name of the domain that you want to connect to, and then click OK. Or, click Browse to select the domain from the domain tree, and then click OK.
- Right-click the domain object, and then click Find.
- In the Find dialog box, click Custom Search.
- Click the domain for which you want to change the functional level.
- Click the Advanced tab.
- In the Enter LDAP query box, type the following and leave no spaces between any characters:
(&(objectCategory=computer)(operatingSystem Version=4*)(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=8192))Note This query is not case sensitive.
- Click Find Now.A list of the computers in the domain that are running Windows NT 4.0 and functioning as domain controllers appears.
A domain controller may appear in the list for any of the following reasons:
- The domain controller is running Windows NT 4.0 and must be upgraded.
- The domain controller is upgraded to Windows Server 2003 but the change is not replicated to the target domain controller.
- The domain controller is no longer in service but the computer object of the domain controller is not removed from the domain.
Before you can change the domain functional level to Windows Server 2003, you must physically locate any domain controller in the list, determine the current status of the domain controller, and then either upgrade or remove the domain controller as appropriate.
Note Unlike the Windows Server 2000 domain controllers, the Windows NT 4.0 domain controllers do not block a level increase. When you change the domain functional level, replication to the Windows NT 4.0 domain controllers will stop. However, when you try to increase to Windows Server 2003 forest level with domains in Windows Server 2000, the mixed level is blocked. The lack of Windows NT 4.0 BDCs is implied by meeting the forest level requirement of all domains at Windows Server 2000 native level or later.
Example: Preparation tasks before the level increase
In this example, the environment is raised from Windows Server 2000 mixed mode to Windows Server 2003 forest mode.
Inventory the forest for earlier versions of domain controllers.
If an accurate server list is not available, follow these steps:
- To discover mixed level domains, Windows Server 2000 domain controllers, or domain controllers with damaged or missing objects, use Active Directory domains and the Trusts MMC snap-in.
- In the snap-in, click Raise Forest Functionality, and then click Save As to generate a detailed report.
- If no problems were found, the option to increase to Windows Server 2003 forest level is available from the “Available Forest Functional Levels” drop down list. When you try to raise the forest level, the domain controller objects in the configuration containers are searched for any domain controllers that do not have msds-behavior-version set to the desired target level. These are assumed to be either Windows Server 2000 domain controllers or newer Windows Server domain controller objects that are damaged.
- If earlier version domain controllers or domain controllers that have damaged or missing computer objects were found, they are included in the report. The status of these domain controllers must be investigated, and the domain controller representation in Active Directory must be repaired or removed by using the Ntdsutil file.
For more information, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
Verify that End to End replication is working in the forest
To verify that End to End replication is working in the forest, use the Windows Server 2003 or newer version of Repadmin against the Windows Server 2000 or the Windows Server 2003 domain controllers:
- Repadmin/Replsum * /Sort:Delta[/Errorsonly] for initial inventory.
- Repadmin/Showrepl * /CSV>showrepl.csv. Import to Excel, and then use the Data->Autofilter to identify replication features.Use replication tools such as Repadmin to verify that forest-wide replication is working correctly.
Verify the compatibility of all programs or services with the newer Windows Server domain controllers and with the higher Windows Server domain and forest mode. Use a lab environment to thoroughly test production programs and services for compatibility issues. Contact vendors for confirmation of capability.
Prepare a back-out plan that includes of one of the following actions:
- Disconnect at least two domain controllers from each domain in the forest.
- Create a system state backup of at least two domain controllers from each domain in the forest.
Before the back-out plan can be used, all domain controllers in the forest must be decommissioned before the recovery process.
Note Level increases cannot be authoritatively restored. This means that all domain controllers that have replicated the level increase must be decommissioned.
After all the previous domain controllers are decommissioned, bring up the disconnected domain controllers or restore the domain controllers from the backup. Remove the metadata from all the other domain controllers, and then re-promote them. This is a difficult process and must be avoided.
| Did you know? Microsoft Edge is the Windows 10 default browser. There are many new tips and tricks that you can learn to improve the user experience. Read: Microsoft Edge User Guide |
Example: How to get from Windows Server 2000 mixed level to Windows Server 2003 forest level
Increase all domains to Windows Server 2000 native level. After this is completed, increase the functional level for the forest root domain to Windows Server 2003 forest level. When the forest level replicates to the PDCs for each domain in the forest, the domain level is automatically increased to Windows Server 2003 domain level. This method has the following advantages:
- The forest-wide level increase is only performed one time. You do not have to manually increase each domain in the forest to the Windows Server 2003 domain functional level.
- A check for Windows Server 2000 domain controllers is performed before the level increase (see preparation steps). The increase is blocked until problem domain controllers are removed or upgraded. A detailed report can be generated by listing the blocking domain controllers and providing actionable data.
- A check for domains in Windows Server 2000 mixed or Windows Server 2003 interim level is performed. The increase is blocked until the domain levels are increased to at least Windows Server 2000 native. Interim level domains must be increased to Windows Server 2003 domain level. A detailed report can be generated by listing the blocking domains.
Windows NT 4.0 upgrades
Windows NT 4.0 upgrades always use interim level during the upgrade of the PDC unless Windows Server 2000 domain controllers have been introduced into the forest the PDC is upgraded into. When interim mode is used during the upgrade of the PDC, the existing large groups use LVR replication immediately, avoiding the potential replication issues that are discussed earlier in this article. Use one of the following methods to get to interim level during the upgrade:
- Select interim level during Dcpromo. This option is only presented when the PDC is upgraded into a new forest.
- Set the forest level of an existing forest to interim, and then join the forest during the upgrade of the PDC. The upgraded domain inherits the forest setting.
- After all the Windows NT 4.0 BDCs are upgraded or removed, each domain must be transitioned to forest level and can be transitioned to Windows Server 2003 forest mode.
A reason to avoid using interim mode is if there are plans to implement Windows Server 2000 domain controllers after the upgrade, or at any time in the future.
Special consideration for large groups in Windows NT 4.0
In mature Windows NT 4.0 domains, security groups that contain far more than 5000 members may exist. In Windows NT 4.0, when a member of a security group changes, only the membership single change is replicated to the backup domain controllers. In Windows Server 2000, group memberships are linked attributes stored in a single multi-valued attribute of the group object. When a single change is made to the membership of a group, the whole group is replicated as a single unit. Because the group membership is replicated as a single unit, there is a potential for updates to group membership to be “lost” when different members are added or removed at the same time at different domain controllers. Additionally, the size of this single object may be more than the buffer used to commit an entry into the database. For more information, see the “Version Store Issues with Large Groups” section of this article. For these reasons, the recommended limit for group members is 5000.
The exception to the 5000 member rule is the primary group (by default this is the “Domain Users” group). The primary group uses a “computed” mechanism based on the “primarygroupID” of the user to determine membership. The primary group does not store members as multi-valued linked attributes. If the primary group of the user is changed to a custom group, their membership in the Domain Users group is written to the linked attribute for the group and is no longer calculated. The new primary group Rid is written to “primarygroupID” and the user is removed from the member attribute of the group.
If the administrator does not select the interim level for the upgrade domain, you must follow these steps before the upgrade:
- Inventory all large groups and identify any groups over 5000, except the domain users group.
- All groups that have more than 5000 members must be broken into smaller groups of less than 5000 members.
- Locate all Access Control Lists where the large groups were entered and add the small groups that you created in step 2.
Windows Server 2003 interim forest level relieves administrators from having to discover and reallocate global security groups with more than 5000 members.
Version store issues with large groups
During long-running operations such as deep searches or commits to a single, large attribute, Active Directory must make sure that the state of the database is static until the operation is finished. An example of deep searches or commits to large attributes is a large group that uses legacy storage.
As updates to the database are continually occurring locally and from replication partners, Active Directory provides a static state by queuing up all incoming changes until the long-running operation is finished. As soon as the operation is finished, the queued changes are applied to the database.
The storage location for these queued changes is referred to as the “version store,” and is approximately 100megabytes. The size of version store varies and is based on the physical memory. If a long-running operation does not finish before the version store is exhausted, the domain controller will stop accepting updates until the long-running operation and the queued changes are committed. Groups that reach large numbers (more than 5000 members) put the domain controller at risk of exhausting the version store as long as the large group is committed.
Windows Server 2003 introduces a new replication mechanism for linked multi-valued attributes that is called link value replication (LVR). Instead of replicating the whole group in a single replication operation, LVR addresses this issue by replicating each group member as a separate replication operation. LVR becomes available when the forest functional level is raised to Windows Server 2003 interim forest level or to Windows Server 2003 forest level. In this functional level, LVR is used to replicate groups among Windows Server 2003 domain controllers. Sources 1,2,3,4,5